Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tool from Google that lets website owners add and manage website tags from a centralised place.
Tags are small blocks of programming code that provide specific functionality to a website. Common examples include:
- Facebook Pixel
- Google Analytics tracking code
- Google Ads conversion tracking code
- Online chat widgets
Tags are commonly related to services that track and measure specific activity on your website or to plugins / widgets from third party providers that deliver niche functionality.
What happened before Google Tag Manager?
Previously, while website owners still wanted these same tags on their website, they were reliant on their website developer to add the necessary code and, if applicable, to configure the tag so that it was only applied on the right occasions.
Google Tag Manager is like a content management system (CMS) for your website's tags
For example, they might want to include a chat widget on their site so customers can chat with them online. But perhaps they don’t want this to appear on the checkout pages in case it interrupts the customer’s buying journey.
In this instance, the website owner relies on their developer to add the relevant tag code to the site and to wrap this within some further code that handles the logic of when the tag should and shouldn’t get implemented.
How does Google Tag Manager benefit me, the website owner?
Google Tag Manager is like a content management system (CMS) for your website's tags. Much as a traditional CMS lets website owners add and update content on their site without needing the technical skills or knowledge to write HTML code, Google Tag Manager lets website owners manage their site’s tags without having to write any code.
How do I add Google Tag Manager to my website?
As a website owner, you can add Google Tag Manager to your website in two steps:
- Create your Google Tag Manager account
- Add your GTM code to each page of your site
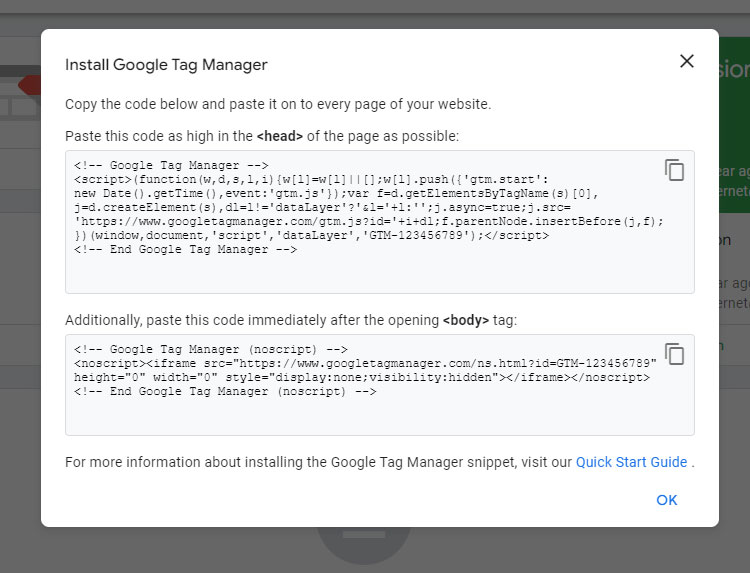
Ironically, even though Google Tag Manager is designed to help non-technical people manage their website’s tags, setting up GTM on a website in the first instance probably does require the help of a technical developer! However, this is a one-off task and once in place, GTM will continue to run across your site and implement any tags you choose to add.
On some occasions, your site’s CMS may manage this process for you and you might only need to add your GTM’s account id to your CMS.
Creating your Google Tag Manager account
This is a straightforward process and you can do it online without needing any payment details.
Your first step is to sign up for an account on the Google Tag Manager website.
Once that’s done, you will have access to a dashboard where you can add tags to your account and set up triggers that control when those tags should fire on your website.
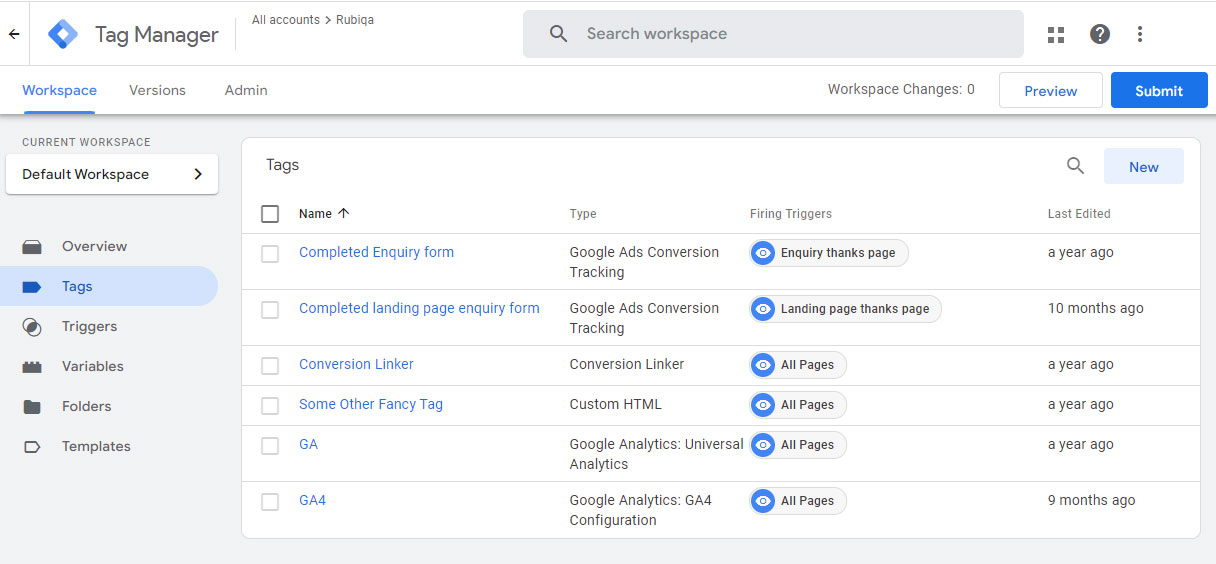
Adding your Google Tag Manager code to your website
To add a tag to your Google Tag Manager account, copy the code from the relevant provider.
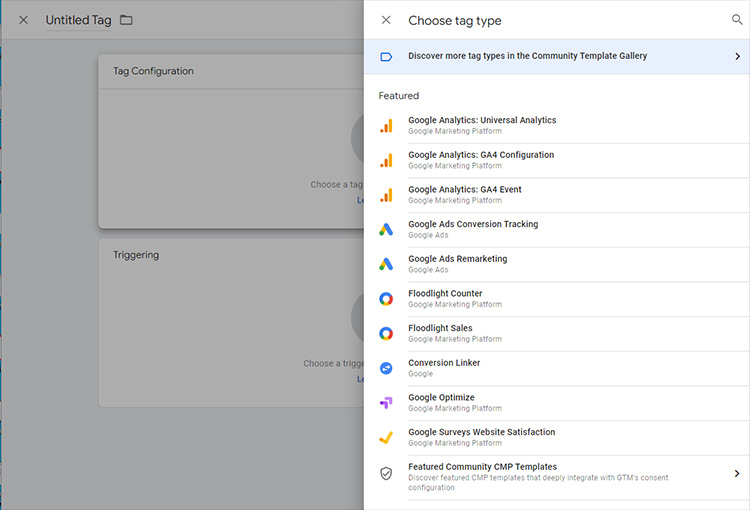
For example, if you want to add your Facebook Pixel to Google Tag Manager, copy the Pixel code from your Facebook account, create a new tag in GTM and paste in that code. When you save it, you’ve created your first tag.
GTM knows that many website owners will want to add similar tags, so commonly-used tags for services such as Google Analytics and Google Conversion tracking are pre-built in GTM and you can add one of these simply by selecting it from the list.
What is a trigger in Google Tag Manager?
Triggers are conditions that define when the tag should be applied to your site. A tag gets "fired” when the conditions of its trigger are fulfilled.
For example, if you want a tag to fire on all pages of your site, you would define a trigger that fires whenever a page view occurs.
If, instead, you only want to fire a tag on your "Contact Us” page, its associated trigger would include a rule that causes it to fire when the page URL is www.yourdomain.co.uk/contact-us, for instance.
Once you have added all the tags and triggers to your account, you should publish those changes so that they become live on your site.
Why you need to use Google Tag Manager on your website
The theory
One of the main benefits of using Google Tag Manager is that it reduces the need to edit code on your website. With Google Tag Manager, you can quickly and easily add tags without having to manually insert scripts into your site. This not only makes it easier to manage your tags but it also reduces the risk of inadvertently introducing coding errors, which could negatively affect your site’s performance.
Google Tag Manager also provides advanced options for managing tags. For instance, by defining suitable triggers, you can set up conditions for when your tags fire. This allows you to create a more refined website experience for your visitors and helps you to better track visitor behaviour across your site.
If you’re not using Google Tag Manager, you will be required to manually add scripts to your website whenever you want to install a new tag.
The reality
Although GTM provides the non-technical person with the means to add and maintain their website’s tags, this can become a false economy. Anything beyond the most standard use-case tends to require a degree of technical knowledge and while you, as the website owner, won’t be required to write programming code to use GTM, you will quickly realise that you need to understand how to configure different triggers, setup GTM variables and manage data sent to Tag Manager’s "dataLayer”.
What is the "dataLayer”?
Think of the dataLayer as a private "holding pen” on your website, where you can deposit data for one of your tags to collect and process.
While Google Tag Manager provides a lot of basic requirements pre-built into its interface, every website is unique and you may want to measure a specific detail on your site that requires a customised approach.
In this instance, you can use GTM’s dataLayer to store data that you pickup and process with one of your tags (e.g. the Google Analytics tag).
So is Google Tag Manager really that much of a benefit to me?
Yes!
Even though you may well find that you’re as dependent on your web developer as you were previously, Tag Manager helps in a number of ways:
- it’s an independent tool, so if you need to change to a different web developer at some point, you can add your new provider as a user on your account and they will be accustomed to your GTM process and setup
- you can test your new tags before you commit them to your live website
- it includes version control, which means that if you / your developer commits something to your website that starts to cause errors, you can roll back to a previous state in your GTM account, fix the issue and then implement it a second time
- it offers more powerful customisation options than is the case without it, particularly if you want your tags to process data in a refined, sophisticated way that reflects your need to analyse data in a bespoke manner
